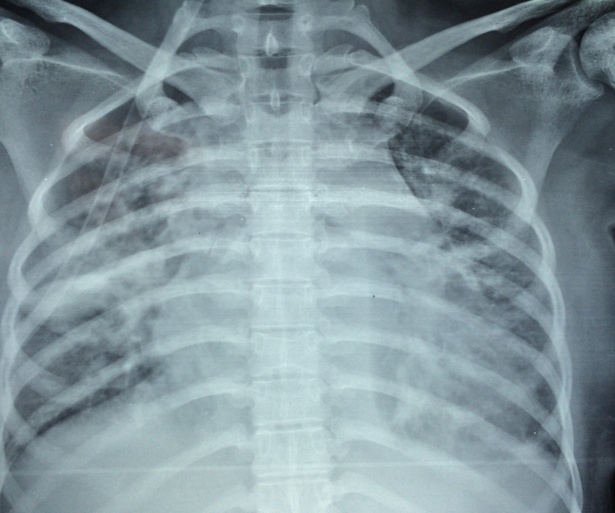
Acute Chest Syndrome (ACS) is a rare but often fatal complication in patients with micro-drepanocytic anemia as in those with beta Sickle Cell Disease (SCD). This case report refers to a female patient with known micro-drepanocytic anemia who was admitted to our ICU due to ACS. Treatment included RBC transfusions with WBC reduction, administration of FFP and plasmapheresis within 48 hours from the ICU admission. At the 3rd ICU day, HbA2 level was found elevated up to 77%. The following ICU days, the patient presented absence of the white series of the blood’s cellular components. After twelve days in the ICU the patient died due to hemodynamic shock and herniation of the brain stem. Given that sickle cell crises are potential precursors of this deadly syndrome, everyday practice should prioritize the prevention of sickle cell crises developing into ACS.
Continue reading

Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome (PRES) is a newly recognised clinical entity, accompanied by characteristic depicted findings. Disturbance of consciousness levels, spasms, vomiting and cortical blindness are the clinical manifestations of the syndrome, while the main causes are hypertensive encephalopathy, renal failure, immunosuppressive and cytotoxic drugs. PRES may be displayed with reversible damage (white matter edema), while if infarcts happen, damage is considered irreversible or neuronal. Early MRI and Diffusion-Weighted MRI (DW-MRI) provide instant information, directly related to a prognosis, as DW-MRI can separate the vasogenic edema from the cytotoxic one, which is accompanied by early infarcts.
Continue reading